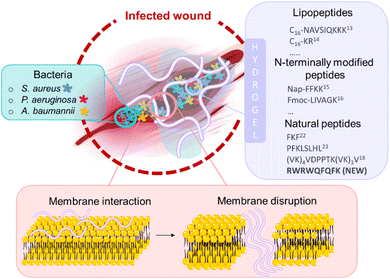
Hydrogel materials have gained considerable interest to be used as aids in the healing of chronic and traumatic wounds, in view of their tunable mechanical stability, biocompatibility and biodegradability. Here, we describe the development of a new injectable and antibacterial peptide-based hydrogel that is composed of only nine natural amino acids. By covalently merging a short antibacterial peptide sequence with a short hydrogelator peptide sequence, the biologically active sequence H-RWRWQFQFK-NH2 was prepared, which self-assembled into a thixotropic hydrogel, a so-called ‘biogel’. This biogel and a related co-formulation of the short antimicrobial peptide H-RWRW-NH2 with the hydrogelating hexamer H-FQFQFK-NH2 were evaluated as potential wound dressings by means of an in vitro wound model using S. aureus, A. baumannii or P. aeruginosa. The obtained data showed that both the biogel and the co-formulation strategy appeared to be particularly effective towards A. baumannii and P. aeruginosa.
Link to Publisher's page: https://doi.org/10.1039/D5RA03481G