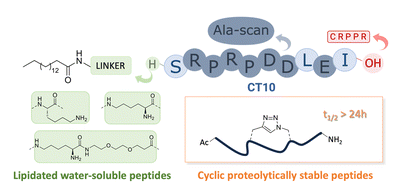
A peptide segment of 10 residues long at the C-terminal (CT) region of Cx43 is known to be involved in interactions, both with the Cx43 protein itself and with other proteins, that result in hemichannel (HC) activity regulation. Previously reported mimetic peptides based on this region (e.g., αCT1, CT10) have revealed to be promising therapeutic agents in the context of cardiovascular disease. In this work, a novel approach to improve the proteolytic stability and increase the bioavailability of the CT10 peptide, such as C- and N- terminal modification and cyclization, is presented. These efforts resulted in a set of unprecedented potent cyclic inhibitors of HC-mediated ATP release with a half-life largely exceeding 24 hours. Additionally, the introduction of a lipophilic moiety with different solubilizing linkers led to the generation of a novel series of water-soluble and lipidated peptides that show high inhibitory capacity in in vitro assays at submicromolar concentrations. Lastly, a cardiac endothelium targeting strategy was adopted, exploiting the CRPPR peptide to selectively deliver the peptides to endothelial cells.
Link to Publisher’s page: