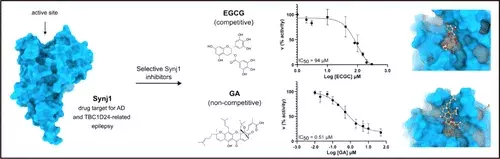
Synaptojanin1 is a presynaptic phosphoinositide phosphatase that harbors two catalytic domains: an N-terminal suppressor of actin 1-like (Sac1) domain that predominantly dephosphorylates PI(3)P and PI(4)P and a central 5-phosphatase (5-PPase) domain that dephosphorylates PI(4,5)P2 and PI(3,4,5)P3. While loss-of-function mutations in Synaptojanin1 are associated with epilepsy and Parkinson’s disease, inhibition of the 5-phosphatase activity of Synaptojanin1 was identified as a potential therapeutic approach for Alzheimer’s disease, Down syndrome, and TBC1D24-associated epilepsy. However, the high conservation of active site residues among the different human 5-phosphatases has hampered the identification of Synaptojanin1-selective inhibitors. Here, we identified epigallocatechin monogallate and gambogic acid as inhibitors of the Synaptojanin1 5-phosphatase activity via a combination of high-throughput screening and structure-based virtual screening. While epigallocatechin monogallate shows promiscuous inhibition of all tested human 5-phosphatase, gambogic acid is selective for Synatojanin1. Correspondingly, kinetic analysis demonstrates that gambogic acid acts as a potent (Ki = 0.51 μM) noncompetitive Synaptojanin1 inhibitor, suggesting that it targets a less conserved allosteric pocket rather than the active site. Together, these findings propose gambogic acid as a promising lead compound for the development of new selective inhibitors of Synaptojanin1.
Link to Publisher's page: Discovery and Characterization of a Selective Inhibitor of Synaptojanin1 5-Phosphatase Activity | ACS Pharmacology & Translational Science